Have you ever launched a new website or published a fresh blog post, only to find it nowhere on Google? It can be super frustrating, especially when you’ve put in hours of hard work. If you’re wondering why your website is not indexed on Google, don’t worry—you’re not alone, and the good news is that it’s usually fixable!
In this blog, we’ll walk you through what indexing means, common reasons your site may not be indexed, and most importantly, how to fix it so your content shows up where it should—on the world’s biggest search engine.
What Does It Mean to Be Indexed by Google?
Before diving into the fixes, let’s understand the basics. When we say a page is “indexed,” it means Google has crawled the page and added it to its database. Only indexed pages can appear in Google search results.
So, if your website or page isn’t indexed, it’s essentially invisible on search—even if everything else is perfect. According to a technical SEO expert, if your website is not showing up on Google search, it’s likely because it hasn’t been indexed yet, or something is blocking Google from doing so.
Common Reasons Your Website Is Not Indexed
There are many reasons a site may not be indexed. Let’s break them down one by one:
a. New Website or URL
If your site is brand new, it may simply be a matter of time. Google doesn’t index all pages instantly. For a new website, Google may take anywhere from a few days to several weeks to crawl and index it. This is a common case of google indexing delay new website.
b. No Sitemap Submitted
Your sitemap is like a roadmap for search engines. It helps them understand the structure of your website. If you haven’t submitted a sitemap, you’re relying solely on Google to discover your pages on its own—and that can be slow.
Learning how to submit sitemap to Google using Google Search Console can speed up the process significantly.
Learn here: how to check sitemap of any website
c. ‘Noindex’ Tag Present
The noindex tag tells Google not to index a page. Sometimes, developers accidentally leave these tags in place when moving from staging to live.
If you’re unsure, it’s worth checking your site’s code or running it through an SEO tool. Then follow best practices on how to fix noindex tag issues.
d. Blocked by Robots.txt
Your robots.txt file controls what Google can and can’t access on your site. If misconfigured, it might be blocking Googlebot from crawling your important pages. This happens more often than people realize.
To fix this, check your robots.txt file and look for disallow rules that shouldn’t be there. This could be the cause of robots.txt blocking Googlebot.
e. Googlebot Can’t Crawl Your Page
Even if your page isn’t blocked, it might still be uncrawlable due to errors like broken links, slow page speeds, or redirects gone wrong. Using Google Search Console indexing issues reports will give you insight into what’s preventing the bot from crawling properly.
f. Duplicate or Low-Quality Content
Google’s algorithm doesn’t want to index duplicate or thin content. If your page is too similar to others—or lacks original value—it may not be indexed at all.
This is especially true for product pages or auto-generated content. Duplicate content and indexing issues go hand-in-hand, so ensure your pages offer something unique.
g. Crawled but Not Indexed Status
Have you seen the dreaded “Crawled – currently not indexed” message in Search Console? This means Google has seen your page, but decided not to include it in its index—for now.
This could be due to low quality signals, poor content, or simply Google testing whether it’s worth indexing. If you’re seeing crawled currently not indexed often, it’s a sign your site needs some content and technical improvements.
How to Fix Indexing Issues
Let’s jump into action. Here are practical steps to help your site get indexed properly:
a. Submit a Sitemap to Google
Head over to Google Search Console and use the “Sitemaps” section to add your sitemap URL (usually something like /sitemap.xml). This helps Google discover all your pages quickly and efficiently.
If you don’t know how, don’t worry—just look up how to submit sitemap to Google and follow Google’s step-by-step instructions.
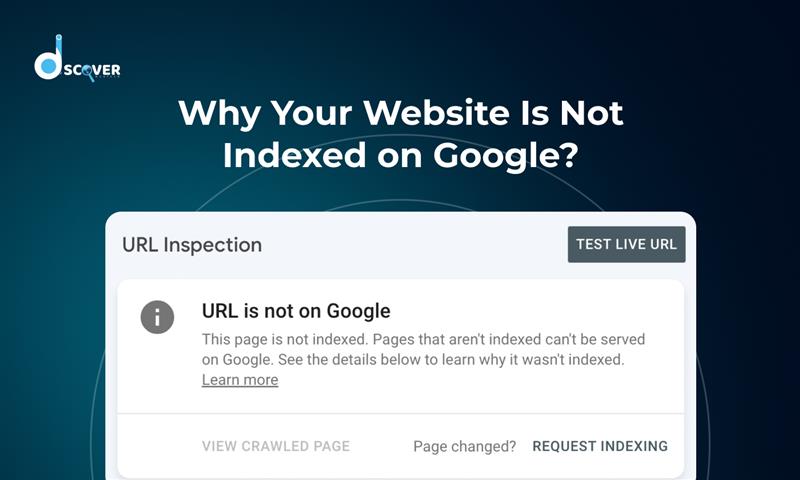
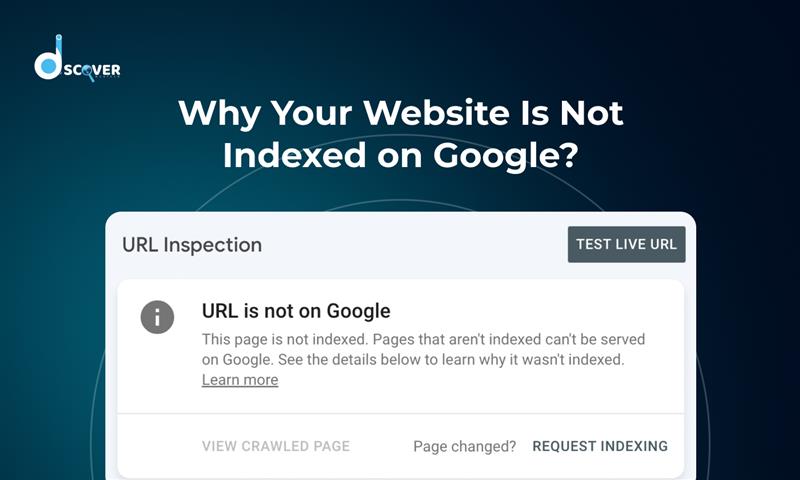
b. Use the URL Inspection Tool
This underrated tool in Search Console lets you manually request indexing. Just paste your page URL and click “Request Indexing.” You can also see if there are crawl issues, rendering problems, or page status updates.
It’s a great first move if your website is not showing up on Google search.
c. Check for Noindex or Robots.txt Issues
Audit your pages for noindex tags using tools like Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, or even browser extensions like SEO Meta in 1 Click. Also double-check your robots.txt file. If you find robots.txt blocking Googlebot, adjust the rules to allow Google access.
Fixing these Google Search Console indexing issues can make a big difference.
d. Improve Content Quality
If Google has crawled your page but isn’t indexing it, try improving the content. Add original images, update text, use internal links, and make it more valuable than what already exists.
Remember: duplicate content and indexing issues often come together. Offer something better and more helpful to users.
e. Increase Internal Linking
One of the best ways to help Google discover your content is by linking to it from already-indexed pages. Internal links act like bridges that guide Googlebot.
By increasing internal links, you reduce the chances of pages being crawled currently not indexed.
f. Fix Technical SEO Errors
Run a technical audit to find crawl errors, slow-loading pages, or redirect chains. Tools like Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, or even free tools like Ahrefs Webmaster Tools can help.
Most indexing issues have technical SEO roots, so even simple fixes can lead to fast results.
Bonus Tips to Speed Up Indexing
Want to give your site an extra push? Try these:
- Build high-quality backlinks: A few relevant backlinks can make Google crawl your site faster.
- Share on social media: Posting your new content on platforms like Twitter or LinkedIn helps with faster discovery.
- Update your content regularly: Fresh content signals to Google that your site is active and worth indexing.
When to Be Concerned (and When Not to Be)
If your site is just a few days old, don’t panic. Google indexing delay for new websites is normal. But if it’s been weeks or months and pages are still not indexed, it’s time to dig deeper using the tips above.
Keep in mind that not all pages need to be indexed, but key pages like your homepage, blog posts, and services should definitely show up.
Final Thoughts
If you’ve made it this far, you now have a solid understanding of why your website is not indexed on Google—and more importantly, how to fix it. Whether it’s a noindex tag, sitemap issue, or robots.txt blocking Googlebot, these problems are usually easy to diagnose and solve.
Take a few minutes to open Google Search Console, check your indexing status, and use this blog as your guide to make the right improvements. With a bit of patience and the right strategies, your site will be live on Google in no time!
Contact us for Digital Marketing Service
Check out our latest blog on: “What Are External Links and Why Do They Matter for SEO?”